Galvanic potential of metals after chromate conversion coating
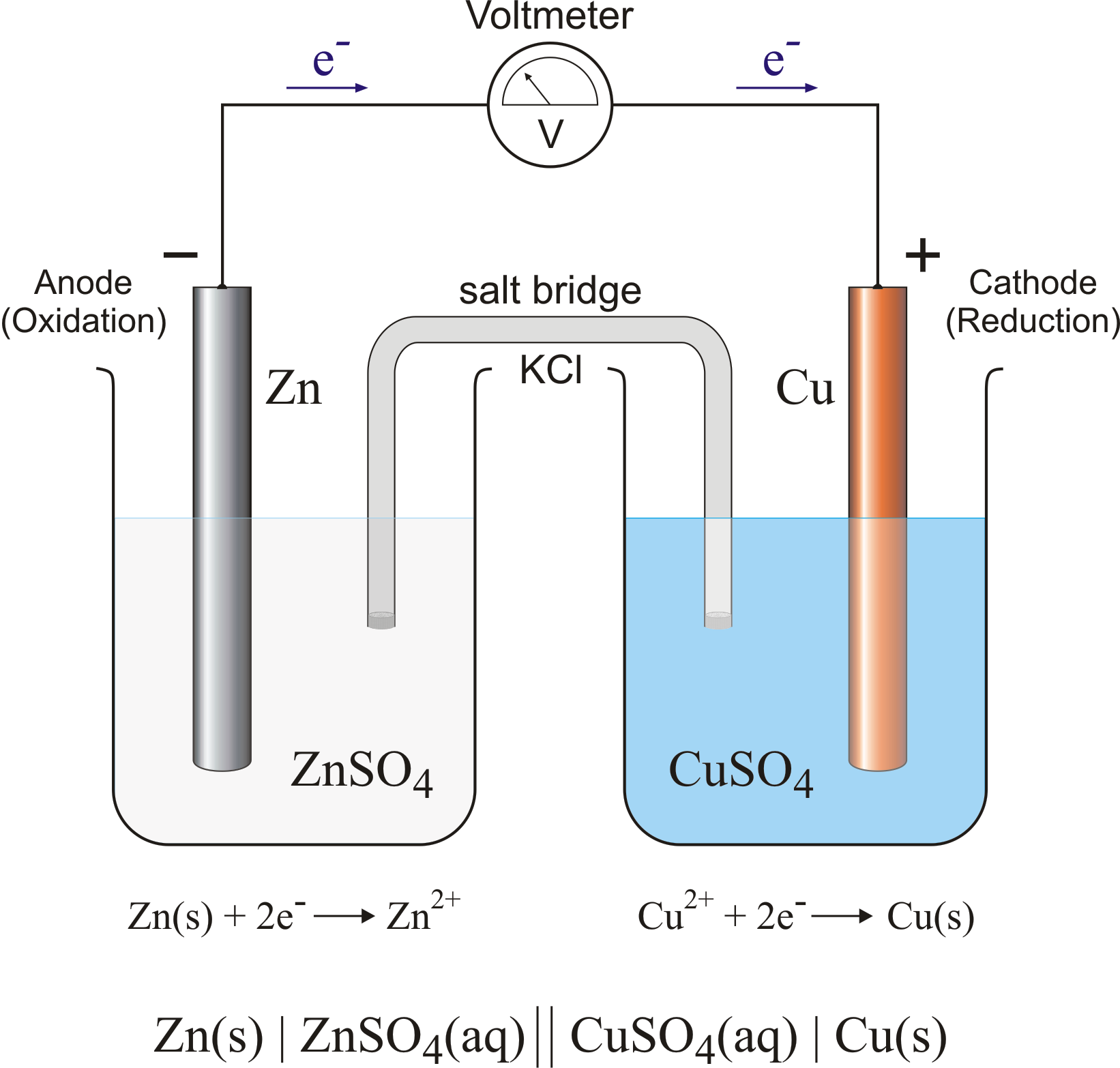
A galvanic (voltaic) cell converts the energy released by a spontaneous chemical reaction to electrical energy. An electrolytic cell consumes electrical energy from an external source to drive a nonspontaneous chemical reaction. Example 2.1.1 2.1. 1. A chemist has constructed a galvanic cell consisting of two beakers.

Galvanic Reaction Chart All Points Fasteners
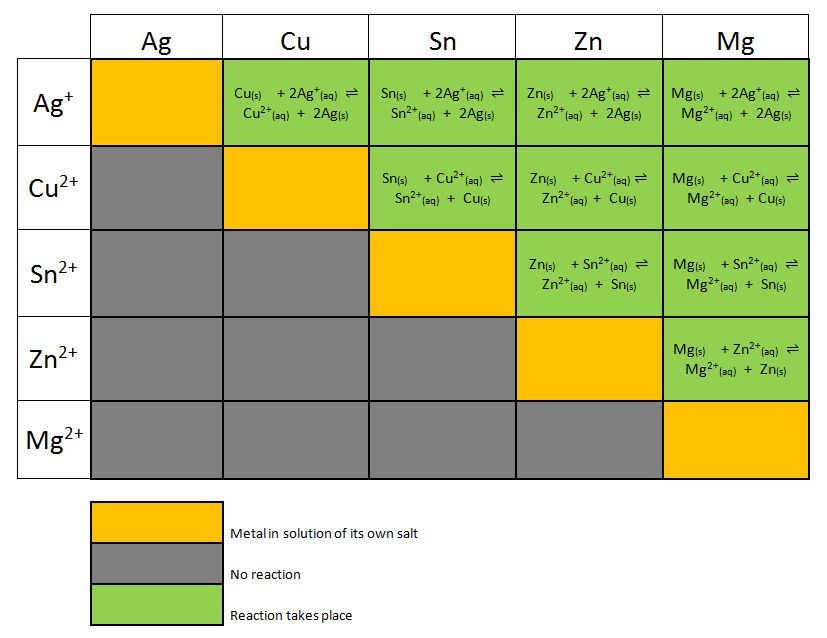
Galvanic corrosion describes a process in which two (or more) dissimilar metals are used together, resulting in a corrosive process. A common application that may experience galvanic corrosion is using an attachment, such as a bolt, that is of a different metal than the primary structure, such as a beam. Table of Contents

Galvanic Corrosion PDF Corrosion Stainless Steel
Corrosion potential and the galvanic series. When a metal corrodes in an electrolyte, atoms from the metal separate into ions and electrons (e - ), with the ions dissolving into the electrolyte. For example, for iron (Fe) the reaction is: Fe → Fe 2+ + 2e −. This is called an anodic reaction and Fe 2+ ions are formed.
Electrochemistry Galvanic Cells and the Nernst Equation
Print. ResearchGate. (2014, March). Galvanic series of various materials in flowing seawater (2.5-4 m/s) at temperatures in the range from 5 to 30oC. [ upload Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Galvanic-series-of-various-materials-in-flowing-seawater-25-4-m-s-at-temperatures-in_fig1_260528991
Solved Consider The Following Galvanic Cells. For Each Ga...
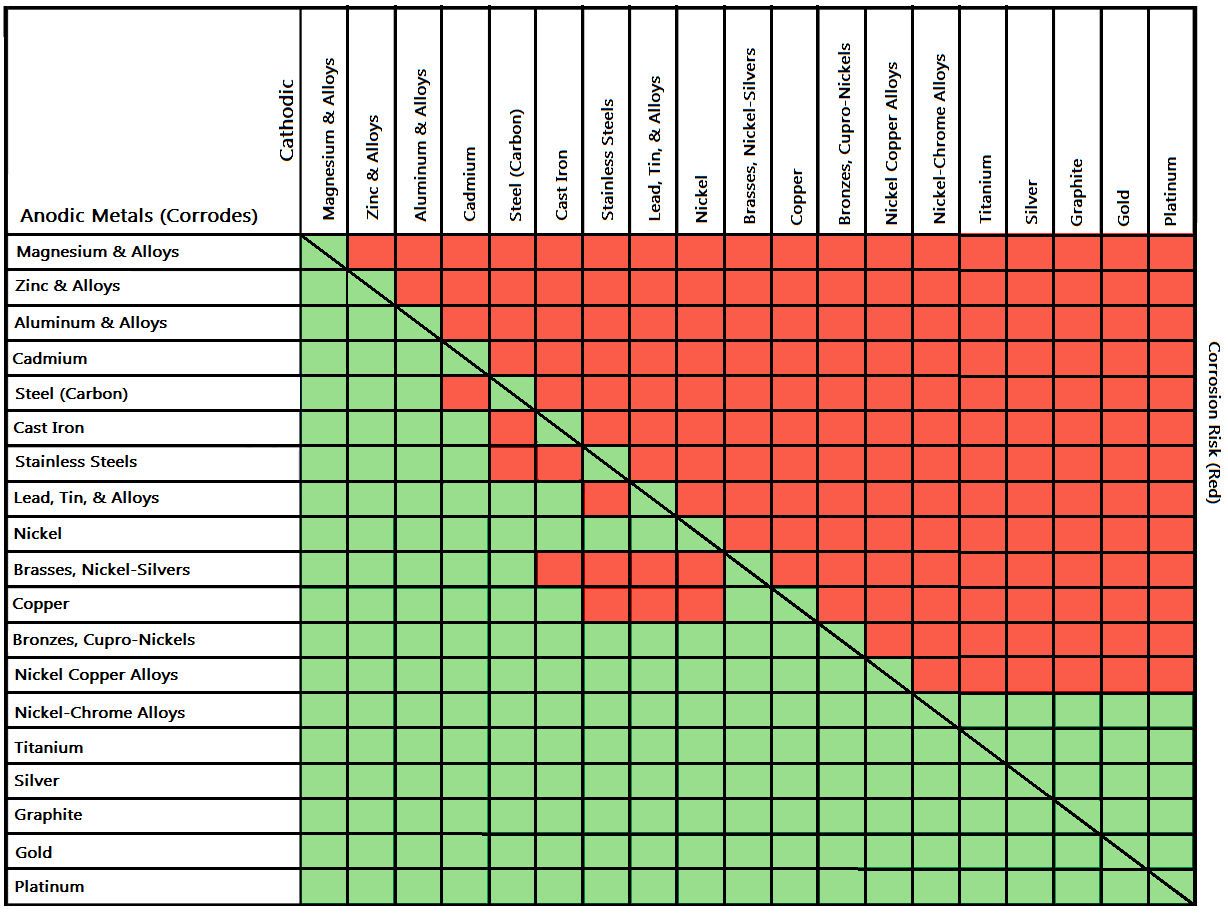
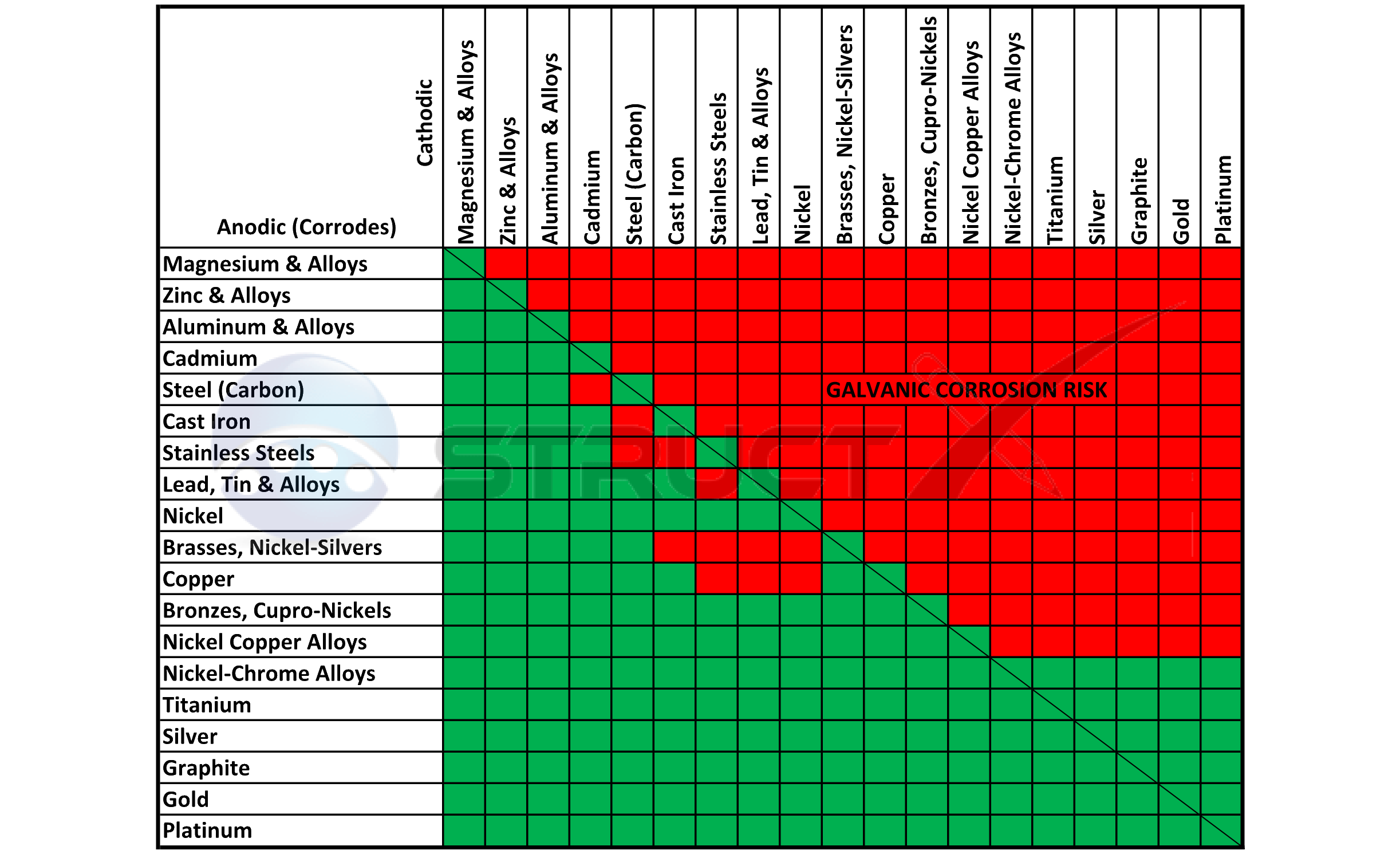
Below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals. Please understand that green represents "lower risk" not "no risk." It should be noted that if sacrificial plating is incorporated in the fastener design, then galvanic action can result in the deterioration of the sacrificial coating, rather than of the fastener.

Separating Galvanic Metals JLC Online
Galvanic or voltaic cells involve spontaneous electrochemical reactions in which the half-reactions are separated (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)) so that current can flow through an external wire. The beaker on the left side of the figure is called a half-cell, and contains a 1 M solution of copper(II) nitrate [Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ] with a piece of copper metal partially submerged in the solution.
Galvanic Corrosion Common Questions Answered
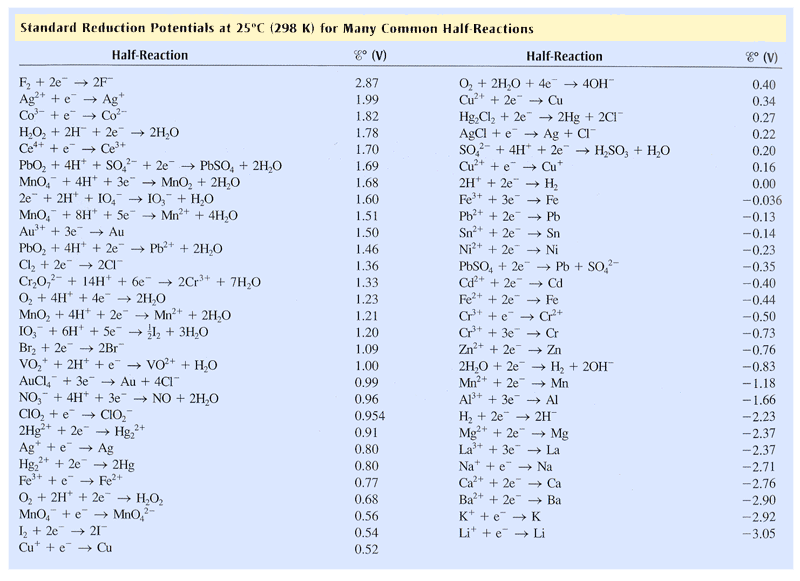
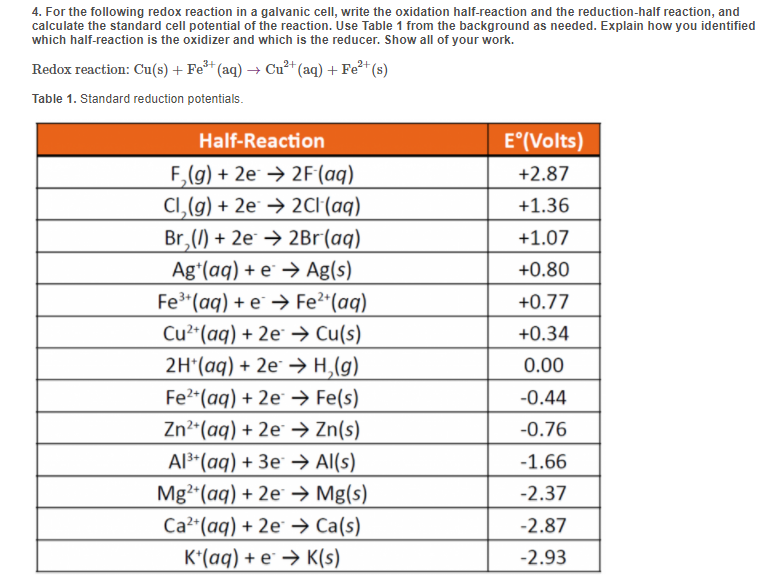
Galvanic reaction is the principle upon which batteries are based. See the table of standard electrode potentials for more details. Galvanic series (most noble at top) The following is the galvanic series for stagnant (that is, low oxygen content) seawater. The order may change in different environments. [1] Graphite Palladium Platinum Gold Silver
Galvanic Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary
Galvanic Table The following galvanic table lists metals in the order of their relative activity in seawater environment. The list begins with the more active (anodic) metal and proceeds down the to the least active (cathodic) metal of the galvanic series.
Galvanic Series (electrochemical series)
75 of The Top 100 Retailers Can Be Found on eBay. Find Great Deals from the Top Retailers. eBay Is Here For You with Money Back Guarantee and Easy Return. Get Your Galvanic Today!
Solved 4. For the following redox reaction in a galvanic
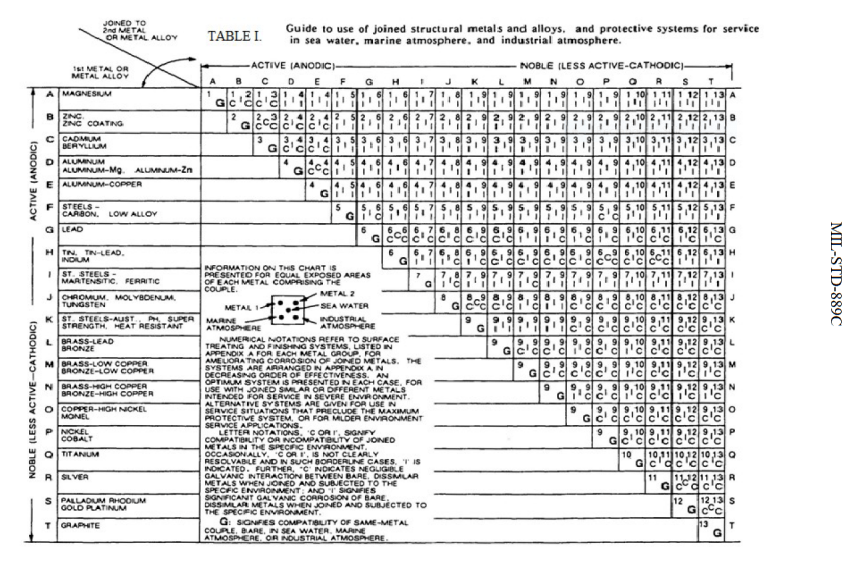
Galvanic series relationships are useful as a guide for selecting metals to be joined, will help the selection of metals having minimal tendency to interact galvanically, or will indicate the need or degree of protection to be applied to lessen the expected potential interactions.

Galvanic Corrosion A Guide for Architects (with a Galvanic Series Chart)
Galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially when it is in electrical contact with another, in the presence of an electrolyte.

Galvanic Corrosion Cable Cleats CMP Products Limited
The table is the galvanic series of metals in sea water from Army Missile Command Report RS-TR-67-11, "Practical Galvanic Series." The Galvanic Table Active (Anodic) Magnesium Mg alloy AZ-31B Mg alloy HK-31A Zinc (hot-dip, die cast, or plated) Beryllium (hot pressed) Al 7072 clad on 7075 Al 2014-T3 Al 1160-H14

The Galvanic Series the essential guide EngineeringClicks
Essentially, galvanic corrosion occurs when two different metals immersed in an electrolyte are joined together. In this scenario, the base or the metal with lesser nobility will undergo corrosion. Thus, the corrosion rate can be determined based on the nobility of metals and the electrolyte to which they're exposed. Advertisement

Galvanic Corrosion [with Chart] EngineerExcel
Shop Like A Billionaire, Come & Check Everything At A Surprisingly Low Price. Come and check everything at a surprisingly low price, you'd never want to miss it.

Galvanic Corrosion Chart Pay attention! You might accidentally learn
The galvanic series determines the electrochemical potential and nobility of metals and metal alloys. Corrosivity Each alloy or metal has a distinctive corrosion potential. The more negative a metal or alloy is, the more likely it is to suffer galvanic corrosion.

Galvanic Corrosion SSINA
up a galvanic action which results in the deterioration of one of them. The following is a list of the more common commercial metals, sequenced according to what is known as the "Galvanic Table": THE GALVANIC TABLE 1. Aluminum 2. Zinc 3. Steel 4. Iron Anodic or Active (+) 5. Nickel 6. Stainless Steel Series 400 ↔ 7. Tin 8. Lead 9. Brass 10.